예외처리
📌 try-catch 문
try catch 구문은 이미 학습한 내용이므로 간단한 예시만 작성하고 빠르게 넘어가겠다!
public class ArrayExceptionHandling {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1};
try{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
// 에러 설명 출력
// Index 1 out of bounds for length 1
System.out.println(e);
System.out.println(e.toString());
// 에러 클래스의 정확한 이름 : 에러 설명
// java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 1 out of bounds for length 1
}
}
}📌 try-catch-finally 문
- 파일이나 네트워크를 닫는 등 리소스 해제 구현시 자주 사용된다.
- try{} 블럭이 실행됐다면 반드시 finally{} 블럭도 실행된다. (try나 catch 블럭에서 return을 한다 해도 반드시 실행된다.)
- 여러 개의 예외 블럭이 있는 경우 각각에서 리소스를 해제하지 않고 finally 블록에서 해제하도록 구현한다.
//ex
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
//return;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
return;
}finally{
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("finally 수행완료");
}📌 try-with-resource 문
try-catch-finally문보다 깔끔하게 리소스를 해제할 수 있다!
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt")){
// 위 try들과는 다르게 try옆에 리소스를 인자로 넣어준다.
System.out.println("read");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) { // IOException은 파일을 닫을 때 발생하는 오류이다. 즉, 자동으로 리소스를 해제해준다.
e.printStackTrace();
}AutoCloseable이라는 인터페이스가 구현돼있기때문에 자동으로 리소스를 해제해준다.
📌AutoCloseable 인터페이스
AutoCloseable인터페이스를 구현한 클래스를 사용해서 리소스가 해제될 때의 동작을 상세하게 설정할 수도 있다. 예시로 간단하게 문구를 출력해보자.
public class MyAutoClose implements AutoCloseable{
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
System.out.println("리소스 closing...");
}
}public class AutoCloseTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyAutoClose myclose = new MyAutoClose();
try(myclose){
// throw new Exception();
} catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("catch!");
}
}
}- 위와 같이
AutoCloseable인터페이스를 구현한MyAutoClose클래스를 생성한 뒤, 이를 try문에 적용해보자! -
try문에서 예외처리가 발생해 catch를 하지않더라도 자동으로 리소스를 해제한다.
[출력결과]
리소스 closing...
-
try문에서 throw를 통해 예외처리가 일어나게 한 뒤 catch를 하더라도 자동으로 리소스를 해제한다.
[출력결과]
리소스 closing...
catch!
예외처리 미루기
- 예외 처리는 예외가 발생하는 문장에서 try-catch 블록으로 처리하는 방법과 이를 사용하는 부분에서 처리하는 방법 두 가지가 있다.
- throws를 이용하면 예외가 발생할 수 있는 부분을 사용하는 문장에서 예외를 처리할 수 있다.
📌 예시
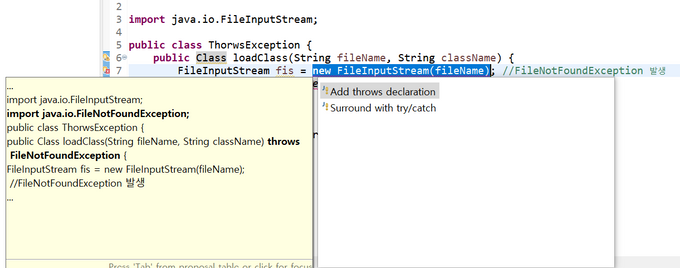
public class ThorwsException {
public Class loadClass(String fileName, String className) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); //FileNotFoundException 발생
Class c = Class.forName(className); //ClassNotFoundException 발생
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}- 위 코드를 작성하면 함수
loadClass내부에 예외처리를 하는 코드가 없으므로 빨간 줄이 쫙 쳐지며 컴파일에러가 난다. - 옆의 전구 아이콘을 클릭하면 다음과 같이 두 가지 해결방안이 뜬다.
- 두 번째 방법은 우리가 지금까지 해왔던 것처럼 try문을 작성해서 함수 내부에 예외처리 구문을 만들어 주는 것이다.
- 첫 번째 방법이 바로 예외처리 미루기인데, 함수옆에 throws를 사용해서 에러를 작성하면 예외처리를 미룰 수 있다.
즉, 해당 함수 구현코드에서 예외처리를 작성하지않고, 실제로 loadClass()를 호출하는 코드에서 예외처리를 하겠다는 말이다.
실제 예외가 발생한 코드내부에서 예외처리를 하는게 좋을지, 해당 예외가 발생할 코드를 호출하는 외부에서 예외처리를 하는게 좋을지는 상황에 따라 다르다고 한다.
public class ThorwsException {
// throws를 사용해서 예외처리를 미룸
public Class loadClass(String fileName, String className) throws FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); //FileNotFoundException 발생
Class c = Class.forName(className); //ClassNotFoundException 발생
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThrowsException test = new ThrowsException();
// loadClass를 호출하는 main메서드에서 예외처리를 함
try {
test.loadClass("a.txt", "java.lang.String");
}catch (FileNotFoundException | ClassNotFoundException e) {// 멀티 예외처리도 가능하다. (에러가 저 중에 하나라도 있으면 실행)
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e){ // 어떤 에러가 나올지 모를 경우 Exception을 사용하면 디폴트로 처리가 가능하다.
// Exception은 모든 예외처리들의 상위클래스이기 때문에 업캐스팅이 된다.
}
}
}사용자 정의 예외 클래스
직접 예외를 만들 수도 있다.
- 기존 예외 클래스중 가장 유사한 예외 클래스에서 상속 받아 사용자 정의 예외 클래스를 만든다.
- 기본적으로 Exception 클래스를 상속해서 만들 수 있다.
public class PassWordException extends IllegalArgumentException{
// 물론 그냥 최상위클래스인 Exception으로 해도 돌아간다.
public PassWordException(String message) {
// message는 에러시 출력되는 문구이다.
super(message);
}
}public class PassWordTest {
private String password;
public void setPassword(String password) {
if (password == null) {
throw new PassWordException("input: "+password+", 비밀번호는 null일 수 없습니다.");
}
else if (password.length() < 8) {
throw new PassWordException("input: "+password+", 비밀번호는 8글자 미만일 수 없습니다.");
}
else if (password.matches("[a-zA-Z]+")) {// 정규 표현식
throw new PassWordException("input: "+password+", 비밀번호는 문자로만 구성될 수 없습니다.");
}
this.password = password;
}
// 테스트 실행
public static void main(String[] args) {
PassWordTest test = new PassWordTest();
String nullpw = null;
String smallpw = "abc1";
String strpw = "aaaaaaaaaaa";
try {
//test.setPassword(nullpw);
test.setPassword(smallpw);
//test.setPassword(strpw);
}
catch(PassWordException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}